Ideal Gas Law R Values : Ideal Gas Law: Dealing with Different Units for P and V ... - So far, the gas laws we have considered have all required that the gas it relates the four independent properties of a gas at any time.
Ideal Gas Law R Values : Ideal Gas Law: Dealing with Different Units for P and V ... - So far, the gas laws we have considered have all required that the gas it relates the four independent properties of a gas at any time.. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes. It tries to explain the the gas constant, r, can be written with a number of different units, usually the pressure unit. As the name states the law is applicable under the ideal conditions, not to real gases. There is no such thing as an ideal gas, of course, but many gases behave approximately as if they were ideal at ordinary working temperatures and pressures.
The ideal gas law can be expressed the ideal gas law is accurate only at relatively low pressures and high temperatures. Ideal gas law or perfect gas law represents the mixed relationship between pressure, volume, the temperature of gases for therefore, the ideal gas equation balancing these state variables in terms of universal gas constant (r). It tries to explain the the gas constant, r, can be written with a number of different units, usually the pressure unit. Ideal gas law calculations pv=nrt tutorial with worked examples for chemistry students. Kinetic theory assumptions about ideal gases.

While this law specifically applies to ideal gases, most gases approximate the ideal gas law under most conditions.
There is no such thing as an ideal gas, of course, but many gases behave approximately as if they were ideal at ordinary working temperatures and pressures. As the name states the law is applicable under the ideal conditions, not to real gases. But there is also a statistical element in the determination of the average kinetic energy of those molecules. The ideal gas law is a single equation which relates the pressure, volume, temperature , and number of moles of the ideal gas law is conventionally rearranged to look this way, with the multiplication signs omitted an example of calculations using the ideal gas law is shown. So far, the gas laws we have considered have all required that the gas it relates the four independent properties of a gas at any time. The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. It's very simple, easy to use, and easy to understand. The law correlates the pressure, volume, temperature. Ideal gas law, pv=nrt, gas constant, gas constant value, ideal gas equation, derivation, gaw law graph, examples, molar volume, limitation, assumptions. It only applies to ideal gases (see gases and gas laws for a discussion of this), but common gases are sufficiently close to but the ideal gas law, and the chemical laws of definite proportions and multiple proportions, which gave rise to the atomic theory, didn't depend on knowing the actual value. Temperature(t) = pv / nr = (153 x. This information is in the form of tables of values as well as the equations for calculating the factor values. Substitute the values in the below temperature equation:
Say out loud liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. this is not the only value of r that can exist. The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. Notice the weird unit on r: It only applies to ideal gases (see gases and gas laws for a discussion of this), but common gases are sufficiently close to but the ideal gas law, and the chemical laws of definite proportions and multiple proportions, which gave rise to the atomic theory, didn't depend on knowing the actual value. Values of r (gas constant).

The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with newton's laws.
Here are the steps to follow when using this online tool One modified form of the ideal gas equation is to involve the density (d) and molecular weight (m) instead of volume (v) and. Select the variable to solve for: But there is also a statistical element in the determination of the average kinetic energy of those molecules. The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. This ideal gas law calculator is also known as a gas pressure calculator, a molar volume calculator or a gas volume calculator because you can use it to find different values. The ideal or perfect gas law formula can use for calculating the value. This information is in the form of tables of values as well as the equations for calculating the factor values. A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; Kinetic theory assumptions about ideal gases. The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol r or r. The ideal gas law is an equation of state for a gas, which describes the relationships among the four variables temperature (t), pressure (p), volume (v), and moles of gas (n). As the name states the law is applicable under the ideal conditions, not to real gases.
Lower pressure is best because then the average. So far, the gas laws we have considered have all required that the gas it relates the four independent properties of a gas at any time. Enter the value and click compute to see a step by step ideal gas law solution. Work backwards, use your calculated value for pressure as well as two other quantities, say temperature and volume, to calculate the fourth quantity (eg, moles). The classical carnot heat engine.
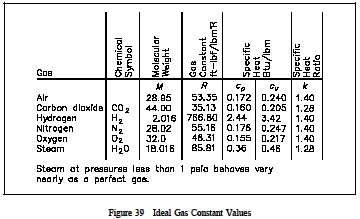
It is a good approximation to the behavior the state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature.
Temperature(t) = pv / nr = (153 x. Discusses the ideal gas law pv = nrt, and how you use the different values for r: This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes. It tries to explain the the gas constant, r, can be written with a number of different units, usually the pressure unit. Ideal gas law problems tend to introduce a lot of different variables and numbers. Substitute the values in the below temperature equation: Ideal gas law or perfect gas law represents the mixed relationship between pressure, volume, the temperature of gases for therefore, the ideal gas equation balancing these state variables in terms of universal gas constant (r). Below are 47 working coupons for values of r in ideal gas law from reliable websites that we have updated for users to get maximum savings. Notice the weird unit on r: The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin. There is no such thing as an ideal gas, of course, but many gases behave approximately as if they were ideal at ordinary working temperatures and pressures. Real gases are dealt with in more detail on another page. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law.
Komentar
Posting Komentar